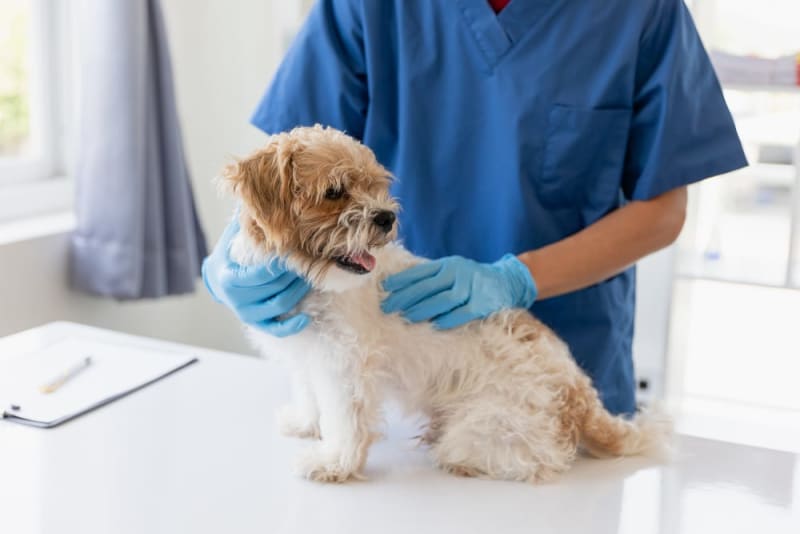
Pets bring immense joy, companionship, and love into our lives. As responsible pet owners, ensuring their health and safety is paramount. One of the most effective ways to protect pets from serious illnesses is through timely and proper pet vaccination. Vaccinations are a cornerstone of preventive care, safeguarding pets from contagious diseases and supporting long-term wellbeing.
Understanding the significance, types, and schedule of pet vaccinations empowers owners to make informed decisions that protect their pets and the broader community.
Why Vaccination Is Crucial for Pets
Vaccinations stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens, preventing infections before they occur. Diseases such as rabies, parvovirus, distemper, and feline leukemia can be life-threatening, but vaccination significantly reduces the risk.
In addition to protecting individual pets, vaccinations also contribute to public health. Preventing the spread of zoonotic diseases—illnesses that can transfer from animals to humans—helps maintain a safer environment for families, other pets, and the community.
Types of Pet Vaccinations
Different pets require different vaccines based on species, age, lifestyle, and health risks. Vaccines are generally categorized into core and non-core types.
Core Vaccines
Core vaccines are recommended for all pets due to the severity and prevalence of the diseases they prevent.
For Dogs:
- Rabies: Prevents a deadly viral infection that can affect both pets and humans.
- Distemper: Protects against a highly contagious and often fatal virus affecting the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems.
- Parvovirus: Prevents a severe and often fatal gastrointestinal disease.
- Adenovirus (Canine Hepatitis): Protects the liver, kidneys, and eyes from viral infection.
For Cats:
- Feline Herpesvirus (Rhinotracheitis): Prevents respiratory infections and eye complications.
- Feline Calicivirus: Protects against oral and respiratory diseases.
- Feline Panleukopenia: Prevents a highly contagious and potentially fatal viral disease.
- Rabies: Protects cats from the deadly rabies virus.
Non-Core Vaccines
Non-core vaccines are given based on a pet’s lifestyle, environment, or specific risk factors. These may include vaccines for:
- Bordetella (kennel cough) in dogs
- Lyme disease
- Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) in cats
- Chlamydophila in cats
Consulting a veterinarian ensures that pets receive the vaccines appropriate for their lifestyle and risk profile.
Vaccination Schedule
A proper vaccination schedule is essential for effective immunity. Puppies and kittens typically receive a series of vaccinations beginning at 6–8 weeks of age, with boosters every 3–4 weeks until they are 16 weeks old. Adult pets require booster shots according to a veterinarian’s recommendations, usually annually or every three years depending on the vaccine type.
Following the correct schedule ensures that the pet’s immune system develops strong and long-lasting protection. Skipping or delaying vaccines can leave pets vulnerable to preventable diseases.
Benefits of Pet Vaccination
Vaccinations provide numerous advantages, including:
- Disease Prevention: Reduces the risk of life-threatening and contagious illnesses.
- Improved Lifespan: Healthy, vaccinated pets tend to live longer and enjoy a better quality of life.
- Community Safety: Prevents the spread of zoonotic diseases to humans and other animals.
- Cost-Effective: Preventing disease is far less expensive than treating serious infections.
- Peace of Mind: Owners can feel confident that their pets are protected against common threats.
Preparing Your Pet for Vaccination
Before vaccination, pets should undergo a wellness check to ensure they are healthy enough for immunization. Factors like fever, illness, or stress may delay vaccination. Owners can prepare pets by:
- Ensuring they are calm and comfortable during the visit
- Bringing a recent health history or vaccination record
- Asking the veterinarian about potential side effects and post-vaccine care
Possible Side Effects
While vaccines are generally safe, some pets may experience mild reactions such as:
- Temporary soreness at the injection site
- Slight fever or lethargy
- Mild loss of appetite
Severe reactions are rare but require immediate veterinary attention. Monitoring pets after vaccination ensures prompt management if any complications arise.
The Role of Veterinarians in Vaccination
Veterinarians play a crucial role in vaccination programs by:
- Assessing each pet’s individual risk factors
- Creating a tailored vaccination schedule
- Administering vaccines safely and effectively
- Monitoring for adverse reactions
- Educating owners on preventive healthcare and ongoing wellness
A trusted veterinarian ensures that vaccinations are up-to-date, effective, and safe for every pet.
Additional Preventive Measures
Vaccination is one element of a comprehensive preventive healthcare plan. Other measures include:
- Regular parasite control
- Balanced nutrition and weight management
- Routine dental care
- Regular exercise and mental stimulation
- Annual wellness check-ups
Integrating these practices with vaccination ensures pets remain healthy and active throughout their lives.
Final Thoughts
Pet vaccination is an essential component of responsible pet ownership. Timely and appropriate vaccines protect pets from life-threatening diseases, contribute to public health, and enhance quality of life.
By consulting a professional veterinarian and following a structured vaccination schedule, pet owners can ensure their companions remain healthy, happy, and protected. Investing in pet vaccination today is an investment in the long-term wellbeing of your beloved animals.